Birthing the Computer Historical Computing Machine 1st Edition by Stephen Kaisler ISBN 9781443885119 1443885118
$50.00 Original price was: $50.00.$35.00Current price is: $35.00.
Birthing the Computer Historical Computing Machine 1st Edition by Stephen H. Kaisler – Ebook PDF Instant Download/Delivery: 9781443885119, 1443885118
Full download Birthing the Computer Historical Computing Machine 1st Edition after payment
Product details:
ISBN 10: 1443885118
ISBN 13: 9781443885119
Author: Stephen H. Kaisler
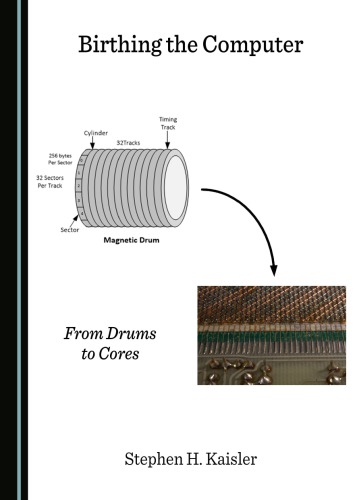
Birthing the Computer: From Drums to Cores examines the evolution of computer systems architecture based on two evolutionary developments: memory technology – magnetic drums to magnetic cores – and CPU technology – transistors. This evolution, exemplified by a number of academic and commercial computing machines, yielded significant performance improvements and more storage leading to more effective utilization. These features would drive the development of programming languages and system software that would enhance the usability of the machines to solve more complex problems in both business, government, and scientific domains. The machines described in this volume represent the leading edge of the transition to second generation computer systems. They introduce a number of key technology concepts in computer architecture and system software that are found in every computer system today, albeit in a more modern form.
Table of contents:
Part I: Magnetic Drum Machines
1. Chapter One
1.1 650 System Architecture
1.1.1 Magnetic Drum Memory
1.1.2 Arithmetic Unit
1.1.3 IBM 650 Self-Checking
1.1.4 IBM 650 Console
1.1.7 IBM 653 High-Speed Core Storage Unit
1.2 IBM 650 Instruction Set
1.2.2 Arithmetic Instructions
1.2.4 Branching Instructions
1.2.6 Miscellaneous Instructions
1.2.8 Index Accumulator Operations Instructions
1.2.9 Floating Point Instructions
1.2.10 IAS Instruction
1.3 IBM 650 Programming
1.4 Symbolic Assembly
1.5 IBM 650 RAMAC
1.6 IBM 650 Assessment
2. Chapter Two
2.1 LGP-30 System Architecture
2.2 LGP-30 Instruction Set
2.3 The Story of Mel
2.5 The LGP-21
2.5.1 LGP-21 System
2.5.2 LGP-21 Memory
2.5.3 LGP-21 Control Registers
2.6 LGP-21 Instruction Set
2.8 LGP-21 Assessment
3. Chapter Three
3.1 Bendix G-15
3.2 G-15 System Configuration
3.2.2 Registers
3.2.4 I/O System
3.3 G-15 Instruction Set
3.3.2 Special Instructions
3.4.1 Magnetic Tape MTA-2
3.4.4 Punched Card Coupler CA-1/CA-2
3.5.1 ALGO
3.5.2 Intercom 1000
3.5.3 Sample G-15 Program
3.6 Tracking Station Application
3.7 G-15 Assessment
Further Reading
Exercises for the Reader
Part II: Core Memory Machines
4. Chapter Four
4.1 BIZMAC System Architecture
4.2 BIZMAC I/O System
4.4 BIZMAC Instruction Set
4.5 BIZMAC Assessment
5. Chapter Five
5.1.1 Central Processor
5.1.2 Program Control
5.1.3 Storage Hierarchy
5.1.4 Virtual Storage
5.3 Atlas Instruction Set
5.3.1 Floating Point Arithmetic Instructions
5.3.2 Indexing Operations
5.3.3 Atlas Branching Instructions
5.3.5 Atlas Odd/Even Test Instructions
5.3.7 Atlas Instruction Example
5.4 Atlas Programming
5.5 The Atlas Supervisor
5.5.1 Structure of the Atlas Supervisor
5.5.2 Job Structure
5.5.4 Process Control
5.5.5 Interrupt Handling
5.6 Atlas 2
5.6.1 Atlas 2 Central Processor
5.6.2 Atlas 2 Memory
5.6.3 Magnetic Tape
5.7 The Atlas 2 Supervisor
5.7.1 Interrupt Routines
5.7.2 Supervisor Extracode Routines
5.7.4 Object Programs
5.8 Atlas Assessment
6. Chapter Six
6.1 JOHNNIAC System Architecture
6.2 JOHNNIAC System Configuration
6.3.1 Conditional Transfer Orders
6.3.2 Transfer Orders
6.3.3 Add Orders
6.3.4 Multiply Operations
6.3.5 Division Orders
6.3.7 Register Movement Orders
6.3.8 Shift Orders
6.3.9 Input/Output Orders
6.3.10 Drum Orders
6.3.12 Control Orders
6.4 JOHNNIAC Operation
6.5 JOSS
6.5.1 JOSS Structure
6.5.2 JOSS Remote Console
6.5.3 JOSS Implementation
6.6 JOHNNIAC Assessment
Further Reading
Exercises for the Reader
Part III: Transistor Machines
7. Chapter Seven
7.1 Solid State Computer Architecture
7.1.1 SSC Central Processor
7.1.2 Magnetic Drum
7.1.3 Operator’s Console
7.2 SSC80/SSC90 Instructions
7.2.3 Transfer Instructions
7.2.5 Comparison Instructions
7.2.8 Card Reader Control Instructions
7.3 SSC Peripherals
7.4.1 FLOW-MATIC
7.5 SSC Assessment
8. Chapter Eight
8.3 Instruction Format
8.3.2 Type II Instructions
8.5 UNIVAC 418-II
8.6 UNIVAC 418-III
8.6.1 UNIVAC 418-III System Architecture
8.6.2 Command/Arithmetic Unit (CAU)
8.6.3 Main Storage
8.6.4 I/O Modules (IOMs)
8.6.5 Magnetic Drums
8.6.7 Communications Systems
8.7 UNIVAC 418 System Software
8.7.1 RTOS Executive
8.7.2 Programming Languages
8.7.3 System Applications
8.8 UNIVAC 418 Assessment
9. Chapter Nine
9.1 UNIVAC 494
9.1 System Architecture
9.1.1 Central Processor
9.1.3 I/O System
9.1.4 Communications Handling
9.1.5 Transfer Switch
9.2 Instruction Set
9.2.1 Shift Instructions
9.2.2 UNIVAC 494 Transfer Instructions
9.2.3 Arithmetic Instructions
9.2.4 Logical Instructions
9.2.5 Comparison Instructions
9.2.6 Jump Instructions
9.2.7 Sequence Modifying Instructions
9.2.8 I/O Instructions
9.3 Peripherals
9.3.1 Magnetic Drums
9.3.4 High-Speed Printer Subsystem
9.4.2 Input Cooperative
9.5 UNIVAC 490/494 Assessment
10. Chapter Ten
10.1.1 TX-0 Registers
10.2 TX-0 Instructions
10.2.1 TX-0 Operate Instructions
10.2.2 Combining Instructions
10.2.3 Modified Instruction Set
10.3 Operating Modes
10.5 FLIT
10.7 TX-2
10.7.1 TX-2 System Architecture
10.8 TX-0 and TX-2 Assessment
11. Chapter Eleven
11.1 Philco 1000
11.1.1 Philco 1000 Central Processor
11.1.3 Instruction Set
11.2 Philco TRANSAC S-2000
11.3 TRANSAC S-2000 System Architecture
11.3.1 Secondary Memory
11.4 TRANSAC S-2000 Instruction Set
11.4.3 Algorithm Control
11.5 Philco 212
11.5.2 Instruction Unit
11.5.3 Index Unit
11.5.4 Arithmetic Unit
11.5.6 I/O Subsystem
11.5.7 Real-Time System
11.5.8 Philco 212 Instruction Set
11.6 Operating System 32KSYS
11.7 TRANSAC S-2000 Software
11.8 Philco 2400 Input/Output System
11.8.1 Philco 2400 System Architecture
11.8.2 Executive Control
11.8.3 Program Control
11.8.5 Main Memory
11.8.6 Operator Control Panel
11.8.8 I/O Operations
11.8.9 Internal Operations
11.8.10 Arithmetic Operations
11.9 Assessment of the Philco Machines
12. Chapter Twelve
12.1 Bendix G-20 System Architecture
12.1.2 Registers
12.1.4 Interrupts
12.2.1 Add/Subtract Operations and Tests
12.2.2 Logic Operations and Tests
12.2.3 Repeated Commands
12.2.5 Storage Operations
12.2.7 Control Operations
12.2.8 I/O Operations
12.2.9 Bus Register Operations
12.4 G-21 Dual Processor
12.5 Bendix G-20 Assessment
13. Chapter Thirteen
13.1 PB250 System Architecture
13.1.1 Central Processor
13.1.2 Main Memory
13.1.3 Flexowriter
13.1.5 HYCOMP 250
13.2 PB250 Commands
13.2.1 Class I Commands
13.2.2 Class II Commands
13.2.4 Class IV Commands
13.2.5 Sequence Tag
13.3 Packard Bell 440
13.3.1 PB440 System Architecture
13.3.2 Memory System
13.3.3 I/O System
13.3.4 PB440 Programming
13.5 Packard Bell Assessment
People also search for:
the birth of computer science
the birth of the computer
a short history of the computer
the birth of computer
the birth of modern computing
Tags: Stephen Kaisler, Birthing the Computer, Computing Machine



